Tech
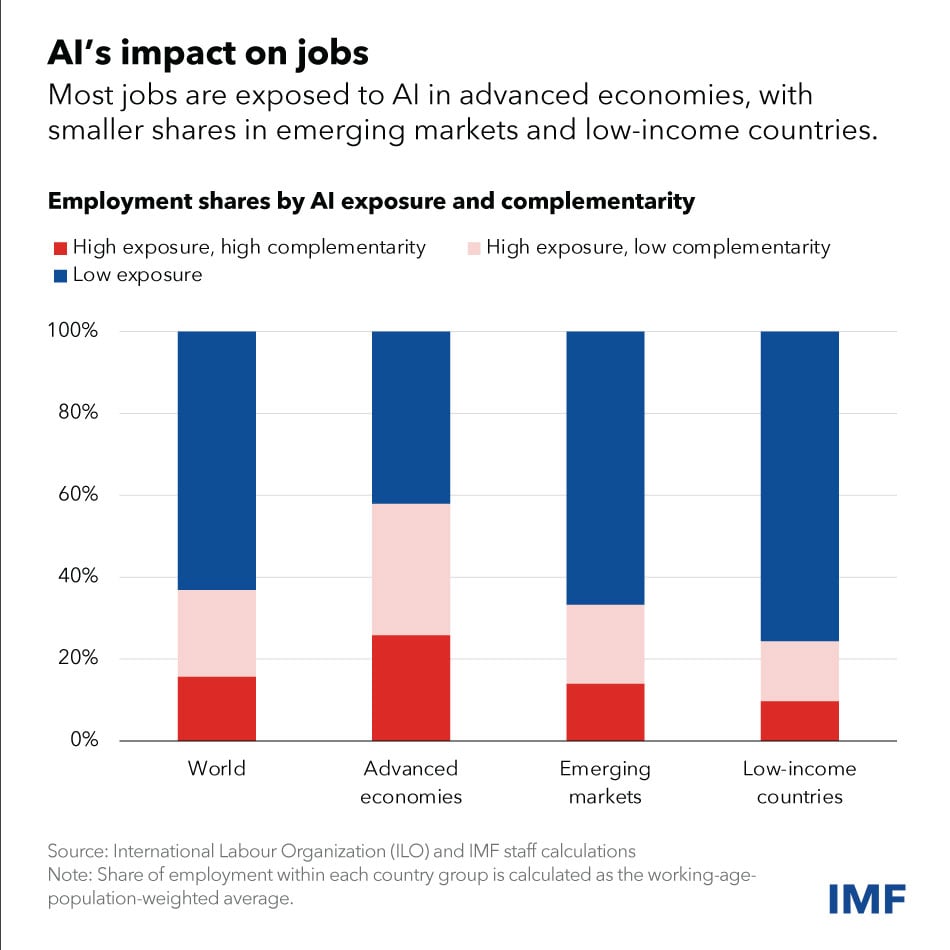
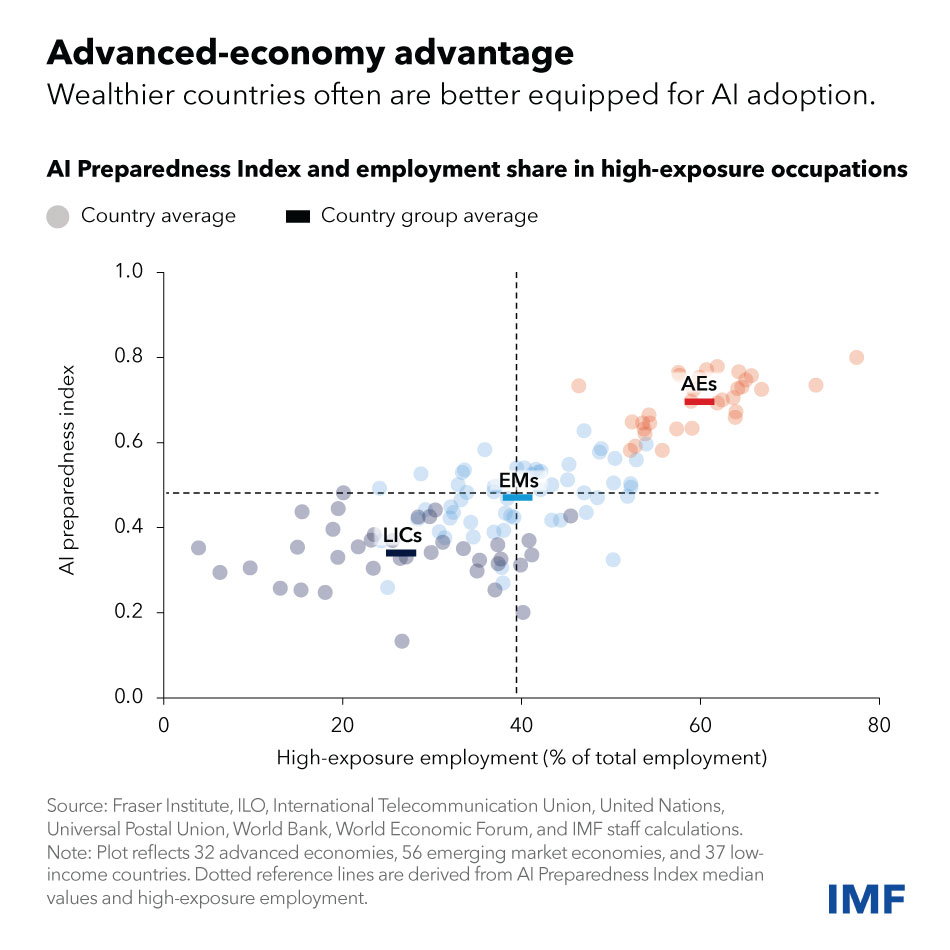
‘Nearly 40% of global employment deemed exposed to AI’
Business
Pakistan’s lunar mission ‘ICUBE-Q’ reaches the moon orbit.
Education
The establishment of IT labs in Islamabad’s educational establishments
Latest News
Pakistan launches first-ever lunar mission with iCube Qamar
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoThere will be no rally in Islamabad on May 9, as police warn of stern action.
-

 Latest News23 hours ago
Latest News23 hours agoCM Maryam resolved to avert tragedies like May 9.
-

 Latest News23 hours ago
Latest News23 hours agoAccording to CPLC data, Karachi saw 4,184 motorbike thefts and 59 fatalities in April.
-

 Latest News23 hours ago
Latest News23 hours agoHajj flight delayed due to airport fire in Lahore
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoHajj 2024: Pakistan’s inaugural flight, carrying 180 pilgrims, departs tomorrow
-

 Latest News23 hours ago
Latest News23 hours agoSher Afzal Marwat has been removed from the PTI’s political committee.
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoThe Uzbek foreign minister comes to Pakistan for a two-day formal visit.
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoPM expresses condolences to UAE President over Sheikh Tahnoun’s death